Columnar Basalt Facts to Shape Your Lesson Plan
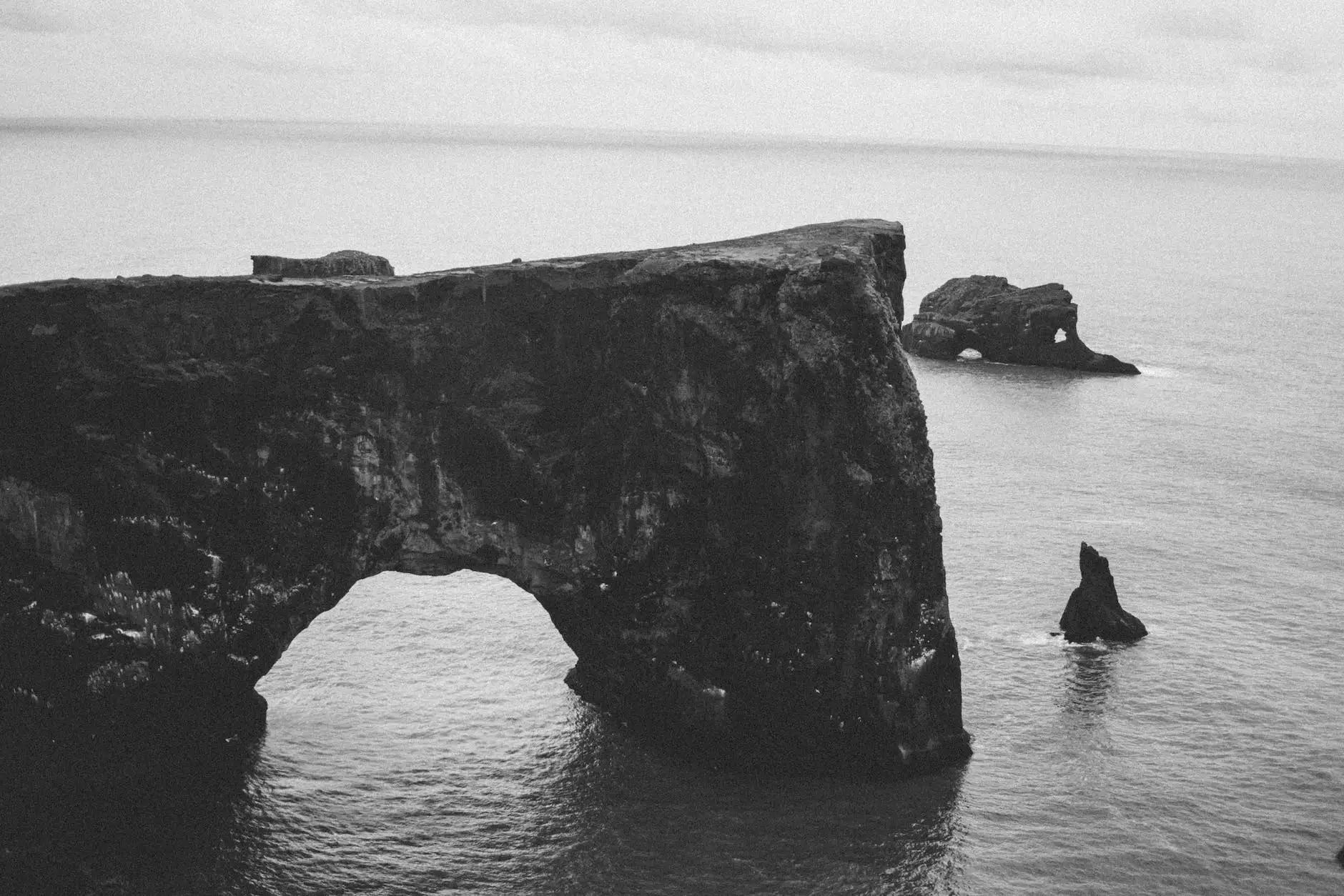

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on columnar basalt, an intriguing geological formation that will surely captivate your students' curiosity. In this article, we will delve into the formation process, unique characteristics, and geological significance of columnar basalt. Let's embark on this exciting journey together!
What is Columnar Basalt?
Columnar basalt is a type of volcanic rock known for its distinct and fascinating hexagonal columnar structure. These geometric columns are formed as lava cools and contracts, creating fractures that divide the rock into vertical columns. The symmetrical appearance of columnar basalt makes it a remarkable natural wonder, often resembling a man-made architectural marvel.
Formation Process
The formation of columnar basalt begins with a volcanic eruption, where molten lava flows across the Earth's surface. As the lava cools, it undergoes a process known as thermal contraction, causing it to shrink and crack. These cracks propagate vertically, resulting in the formation of hexagonal columns. The specific size and shape of the columns are influenced by factors such as cooling rate, lava composition, and underlying geology.
Columnar basalt formations can vary in size, with some columns reaching heights of several meters. The uniformity and precision of the hexagonal columns are a testament to the remarkable natural processes that shape our planet.
Unique Characteristics
One of the most distinctive features of columnar basalt is its hexagonal pattern. While hexagons are the most common shape, variations such as pentagonal or heptagonal columns can also occur, adding an extra layer of intrigue.
Columnar basalt formations are often found near coastlines, cliffs, or volcanic regions, where past eruptions have taken place. The rock itself is usually dark in color, ranging from black to dark gray, and has a fine-grained texture. Its composition primarily consists of minerals like plagioclase feldspar, pyroxene, and olivine.
Another interesting characteristic of columnar basalt is its exceptional durability. Due to the rock's high resistance to weathering and erosion, columnar basalt formations can remain intact for centuries, withstanding the forces of nature.
Geological Significance
Columnar basalt provides valuable insights into past volcanic activity and the Earth's geological history. By studying these formations, geologists can gain a deeper understanding of how lava flows behave during cooling and how geological forces shape the Earth's surface.
Furthermore, columnar basalt can serve as an indicator of environmental conditions during volcanic eruptions. By analyzing the composition and structure of columnar basalt, scientists can reconstruct past volcanic events and make inferences about ancient climates, magma chemistry, and the movement of tectonic plates.
Incorporating Columnar Basalt into Your Lesson Plan
Now that we have explored the captivating world of columnar basalt, let's discuss how you can incorporate this unique geological formation into your lesson plans.
1. Introduce the Formation Process: Start by explaining the volcanic origins of columnar basalt and how its distinctive hexagonal columns are formed through thermal contraction.
2. Discuss Geological Significance: Highlight the importance of columnar basalt in studying past volcanic activity and gaining insights into Earth's geological history.
3. Showcase Real-Life Examples: Utilize visual aids, photographs, or virtual field trips to showcase famous columnar basalt formations around the world, such as the Giant's Causeway in Northern Ireland or Devil's Tower in the United States.
4. Engage in Hands-On Activities: Encourage students to create their own columnar basalt models using clay or other moldable materials. This allows them to better understand the formation process and observe the unique structural properties of columnar basalt.
5. Promote Critical Thinking: Assign research projects or case studies that require students to analyze the geological significance of columnar basalt within a broader context, such as environmental changes or landform development.
By incorporating columnar basalt into your lesson plans, you can ignite your students' curiosity, foster a deeper appreciation for Earth's geological wonders, and inspire the next generation of geologists and scientists.
Conclusion
In conclusion, columnar basalt is an awe-inspiring geological formation that offers a multitude of learning opportunities for both teachers and students. Its unique structure, formation process, and geological significance make it a perfect addition to any geology or Earth science curriculum.
We hope that this comprehensive guide on columnar basalt has equipped you with the necessary insights and knowledge to shape an engaging lesson plan. Embrace the wonders of geology, and let the captivating world of columnar basalt inspire your students to explore the mysteries of our planet!